Pointer in c++ programming language
- Home
- Data types
- Pointer in c++ programming language
- On
- By
- 0 Comment
- Categories: Data types, pointers
Pointer in c++ programming language
Pointer in C++ programming language
The pointer variable is one of the powerful and useful feature in C++ language.
It is one of the most fundamental and important concept in C/C++ language
Pointer function is similar to array in C++/C language but it is not an array. There are many diffrences between them.
Pointer is used to store pieces of data like other variables but it is slighly different.
Pointer variable stores memory address as data similar to array but array is static whereas pointer is dynamic.
We can not change the array size on the program but we can increase or decrease the size of pointer (memory allocation) as per programmers need.
Pointer is a special type of variable used to store the memory address of another variable.

What is a memory unit or address in C?
To understand pointer, you must understand about memory address in C++ language. As we know, a memory unit is a collection of storage cells which can store any type of information.
Each memory cell has a unique value to identify each cell. It’s called address.
If a memory can store n- information, its address ranges from 0 to n-1. That is like an array index.
When we declare a variable in a program, it is assigned a location for storage in a memory.
To store a data in the computer memory , we can use & operator in C/C++ language.
Pointer related operators
var - it is a variable &var - the address of the variable
Find address of memory unit
In the program, we will demonstrate how to find the variable address of memory unit in C++ language.
Example
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "Find address in memory location C++" << endl;
int var_1; //declare variable as int type
int var_2=67;//declare variable and assign value as int type
int var_3=134;
cout<<&var_1<< endl; //display memory address of var_1
cout<<&var_2<< endl; //display memory address of var_2
cout<<&var_3<< endl; //display memory address of var_3
getch();
return 0;
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results
Find address of memory location of values in C++ 0x28ff0c 0x28ff08 0x28ff04
The program displays the address of the memory location that was saved.
In the above output, we can see that the output is displayed in hexa decimal form.
The result may be changed (not same) in different computers. It depends on IDE, platform(processor,O/S) and many more.
We can identify every individual address as it differes by 4bytes. This is because int type variable allocates 4bytes in the computer’s memory(sometimes it may be changed).
Program 2
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int var_1=10; //declare a variable as int
char var_2[10]="Nisa"; //declare a variable as char
float var_3=56.7; //declare a variable as float
cout << "Display every values" << endl;
cout << var_1 << endl;
cout << var_2 << endl;
cout << var_3 << endl;
cout << "\nDisplay address of values" << endl;
cout << &var_1 << endl;
cout << &var_2 << endl;
cout << &var_3 << endl;
getch();
return 0;
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results
Display every values 10 Nisa 56.7 Display address of values 0x28ff0c 0x28ff02 0x28fefc
In the above example & sign used to represent address of variable or value
This displays var_,var_2,var_3’s value and their memory addresses.
Pointer in c++
Pointers variables
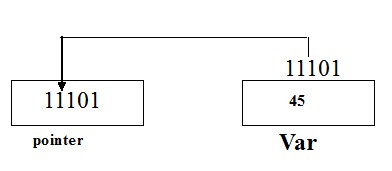
Pointers are used to access and manipulate the data by directly using memory location. We can handle the data and values from the memory location. Pointer variables provide ability to access data using stored memory address.
Pointer variable is one of the type of variable used to hold memory addrees as its data.
Pointer declaration
How to declare a pointer in C++
Syntax
type *var_name;
Example
int *ptr //pointer to int char *ptr2 //pointer to char float *ptr3 //pointer to float
- declare an integer pointer variable to store the memory address of an integer value.
- declare a char pointer variable to store memory address of charactor value.
- declare a float pointer variable to store memory address of float value.
Pointer initialization
int *ptr; //declaration
ptr=&num//initialization
Program 3
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int var_1; //declare a variable as int //1
int *ptr; //declare a pointer variable as int //2
var_1=110; //assign value to variable var_1; //3
ptr=&var_1; //assign the address of var_1 to pointer variable ptr //4
cout <<"The value of var_1 is: "<<var_1 << endl; //5
//Display the value of var_1
cout <<"the address of the value of var_1: "<<&var_1 << endl; //6
//Display the address of the value of var_1
cout <<"the address of the value of var_1: "<< ptr << endl; //7
//Display the address of the value of var_1
cout << "The value of var_1 is: "<<*ptr << endl; //8
//Display the value of var_1
getch();
return 0;
}
The value of var_1 is: 110 The address of the value var_1: 0x28ff08 The address of the value var_1: 0x28ff08 The value of var_1 is: 110
In the above program,
- Declare an integer variable as var_1
- Declare a pointer variable as *ptr
- Assign the value 110 to var_1
- Assign the address of var_1 to ptr using &operator
- Print the value of var_1
- print the address of var_1 (&var_1)
- print the value of ptr – ptr which holds the address of var_1
Similar post
C program to add two numbers using the pointer
C++ program to add two numbers using pointer
C program to find the product of two numbers using the pointer