if statement in Python programming language
if statement in Python programming language
In this tutorial, we will learn about if statement in Python programming language
In the Python programming language, the if..elif..else statement is used for decision making.
If statement in Python
Declaration
Syntax

Flow diagram of if statement in Python

Here, Initially, the program test expression is evaluated by if condition.
When the text expression is true, the body of if statements are executed. When the test expression is false, the flow of control skips the body of if statements and comes out of if body.
Example
//#Example for if statements in Python
age=20; #integer value
if age>18:
print("you are a teen age boy")
//#body of if part
// #if test expression is true, body of if executed
//#if test expression is false, skip execution from if
In the above program, initially, age is initialized by 20.
age >18 is the test expression
When the test expression is evaluated, it returned true, then statements inside the body of if is executed.
When we execute the above program, it will produce the following result
You are a teenage boy
If – else statement in Python
Declaration
Syntax

Initially, the program’s test expression is evaluated by if condition. When the text expression is true, the body of if statements are executed. When the text expression is false, the flow of control skips body of if statements and comes to else part for execution.
Flow diagram of if else statement in python

Program 1
//#this program use to check voting availability based on age
//#using if condition in Python
age=32; //#integer variable
if age>=18: //#if the condition is true, this statement is executed
print("You are allowed to voting")
else: //#if the condition is false, this statement is executed
print("You are allowed to voting");
When we execute the above program, it will produce the following result
you are allowed to voting
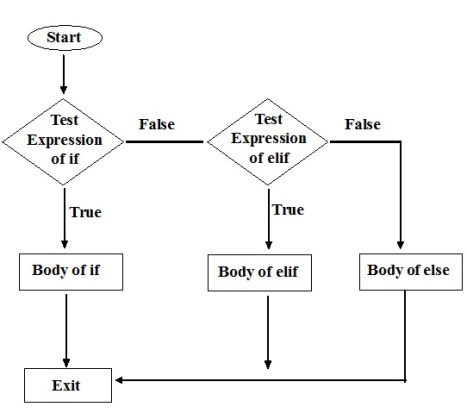
If – elif – else statement in Python
Declaration
Syntax

When the test expression 1 is true, the body of if statement(s) are executed.
When the test expression 1 is false, the flow of control enters the elif part to evaluate test expression 2
when the elif part is true, test expression 2 is executed.
When the test expression 2 is false, test expression moves on to test expression 3
When the test expression 3 is true, the flow of control executes the body of the elif 2 statement(s)
When the test expression 3 is false, the flow of control executes else part statements and exit from the loop.
Flow diagram of if elif – else statement
Program 1
//#Checking number is negative , positive or zero
num=0 //#int variable
if num>0: //#if the condition is true, this statement is executed, if not
print(num," is te positive number");
elif num<0://#if the condition is true, this statement is executed
print(num," is te negative number");
else://#otherwise finally this statement is executed
print("Other one is zero only");
In the above program, variable num is initialized zero(0)
num>0, num<0 are test expressions .
When the var num is positive, positive statements is displayed with the number(if part)
if var num is negative, the negative statement is displayed with the number(elif part)
both statements are false else part statements printed
When we execute the above program, it will produce the following result
Other one is Zero only
Program 2
//#Check natural number 1 -9
x=6 //#integer variable
if x==1:
print("One")
elif x==2:
print("Two")
elif x==3:
print("Three")
elif x==4:
print("Four")
elif x==5:
print("Five")
elif x==6:
print("Six")
elif x==7:
print("Seven")
elif x==8:
print("Seven")
elif x==9:
print("Seven")
else:
print("Zero")
When we execute the above program, it will produce the following result
Zero
Program 3
The model electricity bill is calculated as follows
Electricity bill calculator using if elif else statements in Python
#calculate electicity bill for usage
'''1 - 50 -5/=
51 - 100 - 7/=
101 - 200- 10/=
201 - 300 - 15/=
above 300 - 20/='''
unit = 500 #usage unit
if(unit >0)& (unit <=50):
print("Your bill is",unit*5)
elif(unit >=51)& (unit<=100):
print("Your bill is",50*5+(unit-50)*7)
elif(unit >=101)& (unit<=200):
print("Your bill is",50*5+(100-50)*7+(unit-100)*10)
elif(unit >=201)& (unit<=300):
print("Your bill is",50*5+(100-50)*7+(200-100)*10+(unit-200)*15)
elif(unit >=300):
print("Your bill is",50*5+(100-50)*7+(200-100)*10+(300-200)*15+(unit-300)*20)
When we execute the above program, it will produce the following result
(‘Your bill is’, 7100)
Similar post
If statement in Python language
Suggested for you
Nested for loop in C++ language
Nested while loop in C++ language
Nested for loop in Java language
Nested while loop in Java language
Three dim Array in C++ language
Single dim Array in Java language
Two dim Array in Java language
Three dim Array in Java language
Single dim Array in C language