- On
- By
- 0 Comment
- Categories: Array, Data types
Two dimension Array in C programming language
Two dimensional Array in C programming language
We will learn about Two dimension Array in C programming language
In the C programming language, an array is a data structure which is of fixed size and sequential collection of an element of the same type of data. An array can be used to represent a list of the similar type of elements(eg – list of numbers, list of names).
It is one of the ways to group similar type of elements(data) with a single variable name.
Three type of arrays in C Programming language
- One dimensional Array in C language
- Two dimensional Array in C language
- Three dimensional Array in C language
Two Dimension Array
Declaration of two dimension Array
Syntax
return_type Array_name[size][size];
Example
int marks[4][6]; char alphabet[3][4]; String name[5][6];
2 D array memory representation
This is a Two dimension array named x with 5 rows and 5 column
int array= x[5][5];
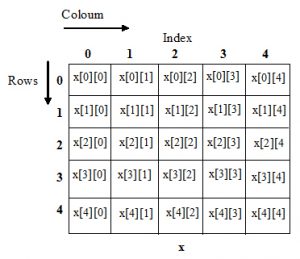
Index is started in zero (0), there fore first index of array – x[0][0]; and last index of array – x[4][4];
How to find an index in two dimension Array
Initializing Two dimension Array
Method 1
arr[0][0]=65; //initialize first elements by value 65
//we can assign the value to every index, like this
Method 2
int age[3][4]={
{23,54,65,76},
{34,65,78,98},
{65,56,43,86}
};
Method 3
int age[3][4]={34,65,78,98,76,54,32,13,15,26,3,38}
more valid declarations
int array_name[2][3]={23,45,65,43,73,32}; //declaration 1 - mentioned above
int array_name[][3]={23,45,65,43,73,32}; //declaration 2
int array_name[2][]={23,45,65,43,73,32}; //declaration 3
int array_name[][]={23,45,65,43,73,32}; //declaration 4
Example for method 1
int marks [4][6]={
{50,71,47,63,58,54} //initialized row index 0
{54,86,37,40,72,51} //initialized row index 1
{96,83,58,52,48,34} //initialized row index 2
{84,69,65,48,63,86} //initialized row index 3
Program 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int array[4][5]={ //Two dimension array
{353,684,653,897,356},
{585,764,809,357,865},
{974,267,836,163,682},
{734,486,263,543,765}
};//declaration & initialization
printf("Output here\n\n");
printf("%d,",array[0][0]);
printf("%d,",array[0][1]);
printf("%d,",array[0][2]);
printf("%d,",array[0][3]);
printf("%d",array[0][4]);
printf("\n");
printf("%d,",array[1][0]);
printf("%d,",array[1][1]);
printf("%d,",array[1][2]);
printf("%d,",array[1][3]);
printf("%d",array[1][4]);
printf("\n");
printf("%d,",array[2][0]);
printf("%d,",array[2][1]);
printf("%d,",array[2][2]);
printf("%d,",array[2][3]);
printf("%d",array[2][4]);
printf("\n");
printf("%d,",array[3][0]);
printf("%d,",array[3][1]);
printf("%d,",array[3][2]);
printf("%d,",array[3][3]);
printf("%d",array[3][4]);
getch();
return 0;
}
When we executed above program, produces the following result
353,684,653,897,356 585,764,809,357,865 974,267,836,163,682 734,486,263,543,765
Program 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int array[4][5]={
{353,684,653,897,356},
{585,764,809,357,865},
{974,267,836,163,682},
{734,486,263,543,765}
};//declaration & initialization
printf("Output here\n\n");
printf("print first row element\n\n");
printf("array[0][0]:%d \n",array[0][0]);
printf("array[0][1]:%d \n",array[0][1]);
printf("array[0][2]:%d \n",array[0][2]);
printf("array[0][3]:%d \n",array[0][3]);
printf("array[0][4]:%d \n\n",array[0][4]);
printf("print second row element\n\n");
printf("array[1][0]:%d \n",array[1][0]);
printf("array[1][1]:%d \n",array[1][1]);
printf("array[1][2]:%d \n",array[1][2]);
printf("array[1][3]:%d \n",array[1][3]);
printf("array[1][4]:%d \n\n",array[1][4]);
printf("print third row element\n\n");
printf("array[2][0]:%d \n",array[2][0]);
printf("array[2][1]:%d \n",array[2][1]);
printf("array[2][2]:%d \n",array[2][2]);
printf("array[2][3]:%d \n",array[2][3]);
printf("array[2][4]:%d \n\n",array[2][4]);
printf("print forth row element\n\n");
printf("array[3][0]:%d \n",array[3][0]);
printf("array[3][1]:%d \n",array[3][1]);
printf("array[3][2]:%d \n",array[3][2]);
printf("array[3][3]:%d \n",array[3][3]);
printf("array[3][4]:%d \n",array[3][4]);
getch();
return 0;
}
When we executed above program, produces the following result
Output here print first row element array[0][0]:353 array[0][1]:684 array[0][2]:653 array[0][3]:897 array[0][4]:356 print second row element array[1][0]:585 array[1][1]:764 array[1][2]:809 array[1][3]:357 array[1][4]:865 print third row element array[2][0]:974 array[2][1]:267 array[2][2]:836 array[2][3]:163 array[2][4]:682 print forth row element array[3][0]:974 array[3][1]:267 array[3][2]:836 array[3][3]:163 array[3][4]:682
Two dimension Array Access using for loop in C language
input element using for loop
for(i=0; i<=3; i++){
for(j=0; j<=4; j++){
scanf("%d",&array_name[i][j])
}
}
Display element using for loop
for(i=0; i<=3; i++){
for(j=0; j<=4; j++){
printf("%d",array_name[i][j])
}
}
Example
Program 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int array[2][4]={{23,45,65,43},{54,87,76,32}};
int i,j;
for (i=0; i<2; i++){
for(j=0; j<4; j++){
printf("%d\n",array[i][j]);
}
}
return 0;
}
When we executed above program, produces the following result
23 45 65 43 54 87 76 32
Program 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[3][4];
int i,j;
for (i=0; i<=2; i++){
for(j=0; j<=3; j++){
//ask input from user
printf("Enter the value for marks[%d][%d] :",i,j);
scanf("%d",&marks[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\n here display marks :\n");
for (i=0; i<=2; i++){
for(j=0; j<=3; j++){
printf("marks[%d][%d] :%d\n",i,j,marks[i][j]);
}
}
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute the above program, it produces the following result
Enter the value for marks[0][0] :45 Enter the value for marks[0][1] :67 Enter the value for marks[0][2] :98 Enter the value for marks[0][3] :64 Enter the value for marks[1][0] :79 Enter the value for marks[1][1] :94 Enter the value for marks[1][2] :36 Enter the value for marks[1][3] :73 Enter the value for marks[2][0] :26 Enter the value for marks[2][1] :60 Enter the value for marks[2][2] :48 Enter the value for marks[2][3] :37 here display marks : marks[0][0] :45 marks[0][1] :67 marks[0][2] :98 marks[0][3] :64 marks[1][0] :79 marks[1][1] :94 marks[1][2] :36 marks[1][3] :73 marks[2][0] :26 marks[2][1] :60 marks[2][2] :48 marks[2][3] :37
Two dimension Array Access using while loop in C language
input element using while loop
while(i<=2){
while(j<=2){
scanf("%d",&array_name[i][j])
}
}
Display element using while loop
while(i<=2){
while(j<=2){
printf("%d",&array_name[i][j])
}
}
Program 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[3][4]={
{56,73,79,92},
{39,95,72,47},
{49,71,75,32},
};
int i=0;
while(i<=2){
int j=0;
while(j<=3){
printf("%d\n",marks[i][j]);
j++;
}
i++;
}
printf("End the program\n");
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute above program, it produces the following result
56 73 79 92 39 95 72 47 49 71 75 32 End the program
Program 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[3][4];
int i=0;
printf("Enter the values for marks\n");
while(i<=2){
int j=0;
while(j<=3){
scanf("%d",&marks[i][j]);
j++;
}
i++;
}
int k=0;
printf("Your marks here\n");
while(k<=2){
int l=0;
while(l<=3){
printf("%d\n",marks[k][l]);
l++;
}
k++;
}
printf("End the program\n");
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute the above program, it produces the following the result
Enter the value for marks 56 67 78 89 90 98 87 76 46 73 42 37 Your marks here 56 67 78 89 90 98 87 76 46 73 42 37
Similar post
Three dim Array in C++ language
Single dim Array in Java language
Two dim Array in Java language
Three dim Array in Java language
Single dim Array in C language
Suggested for you
Nested for loop in C++ language
Nested while loop in C++ language
Nested for loop in Java language
Nested while loop in Java language