- On
- By
- 0 Comment
- Categories: Array, Data types
Three dimension Array in C programming language
Three dimensional Array in C programming language
In this tutorial, we will discuss Three dimension Array in C programming language
In the C programming language, an array is a fixed size of a sequential collection of elements of the same data type. An array can represent a list of number(int), name(String), floating point value or another data type of similar elements. It is one of the way of grouping similar type of data in a single unit
There are three type of array in C programming language
- One dimension array
- Two dimension array
- Three dimension array
Three dimension array in C
Collection of two-dimensional arrays create a three-dimensional array. The multidimensional array can be defined as an array of arrays
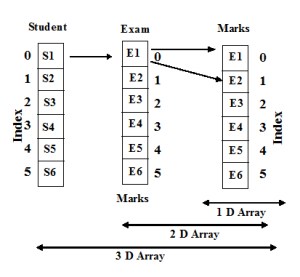
Three-d array is one of the complex data structure
Declaration of three dimension array
Syntax
Data_type Array_name[size][size][size];
Example -1 integer array
int marks[2][3][4];
Example -2 char array
char alphabet[4][3][3];
initializing methods
method 1
Syntax for initialization
array_name[index_1][index_2][index_3]=value;
Example for initialization
age[0][0][0]=34;//first element of array
// we can assign the value to every index, like this
Display element of an array
printf(array_Name[index_1][index_2][index_3]);
Example
printf(marks[0][0][0]); //display first element of array
program 1
Initializing and printing every element based in an index
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int age[2][2][3];//Array declaration
printf("Simple example for 3D array in C\n\n");
age[0][0][0]=46;//Initiation
age[0][0][1]=52;
age[0][0][2]=23;
age[0][1][0]=12;
age[0][1][1]=27;
age[0][1][2]=36;
age[1][0][0]=67;
age[1][0][1]=53;
age[1][0][2]=26;
age[1][1][0]=36;
age[1][1][1]=45;
age[1][1][2]=56;
printf("age[0][0][0] value is :%d\n",age[0][0][0]);
printf("age[0][0][1] value is :%d\n",age[0][0][1]);
printf("age[0][0][2] value is :%d\n",age[0][0][2]);
printf("age[0][1][0] value is :%d\n",age[0][1][0]);
printf("age[0][1][1] value is :%d\n",age[0][1][1]);
printf("age[0][1][2] value is :%d\n",age[0][1][2]);
printf("age[1][0][0] value is :%d\n",age[1][0][0]);
printf("age[1][0][1] value is :%d\n",age[1][0][1]);
printf("age[1][0][2] value is :%d\n",age[1][0][2]);
printf("age[1][1][0] value is :%d\n",age[1][1][0]);
printf("age[1][1][1] value is :%d\n",age[1][1][1]);
printf("age[1][1][2] value is :%d\n",age[1][1][2]);
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute the above program, it produces the following result
Simple example for 3D array in C age[0][0][0] value is :46 age[0][0][1] value is :52 age[0][0][2] value is :23 age[0][1][0] value is :12 age[0][1][1] value is :27 age[0][1][2] value is :36 age[1][0][0] value is :67 age[1][0][1] value is :53 age[1][0][2] value is :26 age[1][1][0] value is :36 age[1][1][1] value is :45 age[1][1][2] value is :56
At the above program, there is a three-dimension Array printed by index base.
method 2
Initializing the whole element in few lines and printing every element in index base
Example for initialization
int marks=[2][3][4]= //declaration
{
{45,67,54,34},{98,65,6,43},{92,48,62,57}},//initialization
{{67,23,81,45},{70,54,27,83},{67,03,51,82,}}
};
program 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[2][3][2]={
{{34,57},{77,79},{64,68}},
{{62,53},{25,83},{36,76}},
};
printf("marks[0][0][0]=%d\n", marks[0][0][0]);
printf("marks[0][0][1]=%d\n", marks[0][0][1]);
printf("marks[0][1][0]=%d\n", marks[0][1][0]);
printf("marks[0][1][1]=%d\n", marks[0][1][1]);
printf("marks[0][2][0]=%d\n", marks[0][2][0]);
printf("marks[0][2][1]=%d\n", marks[0][2][1]);
printf("marks[1][0][0]=%d\n", marks[1][0][0]);
printf("marks[1][0][1]=%d\n", marks[1][0][1]);
printf("marks[1][1][0]=%d\n", marks[1][1][0]);
printf("marks[1][1][1]=%d\n", marks[1][1][1]);
printf("marks[1][2][0]=%d\n", marks[1][2][0]);
printf("marks[1][2][1]=%d\n", marks[1][2][1]);
getch();
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute the above program, it produces the following result
marks[0][0][0]=34 marks[0][0][1]=57 marks[0][1][0]=77 marks[0][1][1]=79 marks[0][2][0]=64 marks[0][2][1]=68 marks[0][0][0]=62 marks[1][0][1]=53 marks[1][1][0]=25 marks[1][1][1]=83 marks[1][2][0]=36 marks[1][2][1]=76
initializing using nested for loop
for(i=0; i<arraysize1;i++){
for(j=0; j<arraysize2;j++){
for(k=0; k<arraysize3;k++){
scanf("%d",&array_name[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
Display element using nested for loop
for(i=0; i<2;i++){
for(j=0; j<3;j++){
for(k=0; k<4;k++){
printf("%d",marks[i][j][k])
}
}
}
Program 3
initializing every element usingnested for loop and printing every element using nested for loop
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[3][2][2];//array declaration in C
int i,j,k;//variable declaration
printf("Enter the elements of the array\n");
for(i=0; i<3; i++){
for(j=0; j<2; j++){
for(k=0; k<2; k++){
printf("marks[%d][%d][%d]=",i,j,k);
scanf("%d",&marks[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
printf("..................\n\n");
printf("Display entered elements\n\n");
for(i=0; i<3; i++){
for(j=0; j<2; j++){
for(k=0; k<2; k++){
printf("marks[%d][%d][%d]=\n",i,j,k,marks[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute the above program, it produces the following result
Enter elements of array marks[0][0][0]=36 marks[0][0][1]=42 marks[0][1][0]=58 marks[0][1][1]=93 marks[1][0][0]=16 marks[1][0][1]=79 marks[1][1][0]=83 marks[1][1][1]=48 marks[2][0][0]=72 marks[2][0][1]=39 marks[2][1][0]=63 marks[2][1][1]=26 ......................... Display entered elements marks[0][0][0]=36 marks[0][0][1]=42 marks[0][1][0]=58 marks[0][1][1]=93 marks[1][0][0]=16 marks[1][0][1]=79 marks[1][1][0]=83 marks[1][1][1]=48 marks[2][0][0]=72 marks[2][0][1]=39 marks[2][1][0]=63 marks[2][1][1]=26
Program 4
initializing every element using nested for loop and printing every element using nested while loop
Display element using nested while loop in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[2][3][4]={
{{45,67,87,43},{46,35,79,26},{52,48,55,66}},
{{25,57,97,43},{57,27,54,44},{66,79,50,59}},
};
int i=0;
while(i<=1){
int j=0;
while(j<=2){
int k=0;
while(k<=3){
printf("Students marks is :%d\n",marks[i][j][k]);
k++;
}
j++;
}
i++;
}
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute above program, it produces the following result
Student marks is :45 Student marks is :67 Student marks is :87 Student marks is :43 Student marks is :46 Student marks is :35 Student marks is :79 Student marks is :26 Student marks is :52 Student marks is :48 Student marks is :55 Student marks is :66 Student marks is :25 Student marks is :57 Student marks is :97 Student marks is :43 Student marks is :57 Student marks is :27 Student marks is :54 Student marks is :45 Student marks is :44 Student marks is :66 Student marks is :79 Student marks is :50 Student marks is :59
Program 5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int marks[2][2][3];
int i=0;
printf("Enter student marks to array\n");
while(i<=1){
int j=0;
while(j<=1){
int k=0;
while(k<=2){
scanf("%d",&marks[i][j][k]);
k++;
} j++;
} i++;
}
printf("\nHere your student marks\n\n");
int m=0;
while(m<=1){
int n=0;
while(n<=1){
int l=0;
while(l<=2){
printf("marks[%d][%d][%d]= %d\n",m,n,l, marks[m][n][l]);
l++;
}
n++;
}
m++;
}
getch();
return 0;
}
When we execute above program, it produces the following result
Enter student marks to array 45 67 78 98 70 84 37 62 50 61 37 89 Here your student marks marks[0][0][0]=45 marks[0][0][1]=45 marks[0][0][2]=45 marks[0][1][0]=45 marks[0][1][1]=45 marks[0][1][2]=45 marks[1][0][0]=45 marks[1][0][1]=45 marks[1][0][2]=45 marks[1][1][0]=45 marks[1][1][1]=45 marks[1][1][2]=45
Similar post
Three dim Array in C++ language
Single dim Array in Java language
Two dim Array in Java language
Three dim Array in Java language
Single dim Array in C language
Suggested for you
Nested for loop in C++ language
Nested while loop in C++ language
Nested for loop in Java language
Nested while loop in Java language