- On
- By
- 0 Comment
- Categories: Array, Data types
Single dimensional Array in Java language
Single dimensional Array in Java language
Single dimension Array in Java language
We will learn about Single dimensional Array in Java language
The array is a data type in Java. It is a collection of similar type of elements that have contiguous index based memory location. We can use one-dimensional array to store a fixed set of elements(single dimension) in Java programming language.
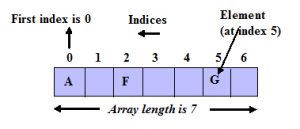
Always, Array index is starting from 0, not 1
Array index ending at n-1(n denotes array length)
Array length(size) starts from 1 and ends at n(n is array length)
Array declaration, creation, initiation
Declaration of single dimension Array in Java
Syntax
We can declare one dimension Array following 3 ways
method_1 - data_type[] array_name; method_2 - data_type []array_name; method_3 - data_type array_name[];
Examples
int[] number; //Exmple 1 int []number; //integer array to save only integer value int number[];
double[] zsore; //Exmple 2 double []zsore; //double array to save only floating point value double zsore[];
String[] name; //Exmple 3 String []name; //String array to save only String value String name[];
- The data type can be a primitive data type similar int, char, double, byte etc.. or an object
- An array name is an identifier
Creating a single dimension Array in Java
We can create one dimensional Array as follows
syntax
array_name=new data_type[array_length];
Example
number=new int[5];
Here, the number is an array name that can hold five number of integer values
Declaration and creation in single line
We can declare and create one dimensional Array in one line as follows
syntax
data_type []array_name=new data_type[array_length];
Example
int []number=new int[5];
Memory representation of this array
Initialization of single dimension Array in Java
We can initialize one dimensional Array as follows- index based
Method 1
Syntax
array_name[0]=element_1; array_name[1]=element_2; array_name[2]=element_3; array_name[3]=element_4;
Example
number[0]=23; //first element of array number[1]=45; //second element of array number[2]=76; //third element of array number[3]=25; //forth element of array
Method 2
Syntax
int[] array_name={element_1, element_2, element_3,........., element_n }
Example
int[] marks={34,67,84,25,68,98}
typically, array length is determined by the number of values. – array length of this array is 6
At this example, we provided six values, so array length is 6, this array can hold 6 values
array length cannot be changed in the program
Memory representation of this array
Default values of the array
After the array is declared, (before to initialize) array will be filled every array index with default values in memory locations.
the default value is 0 for numeric type, null for String and false for boolean type
Example
class Array_Default{
public static void main(String args[]){
String[] names=new String[5];//array is declared, but not initilized
System.out.println(names[0]);
System.out.println(names[1]);
System.out.println(names[2]);
System.out.println(names[3]);
System.out.println(names[4]);
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
null null null null null
Display array elements after initialization
Program 1
class array_1dim{
public static void main (String args[]){
int x[]=new int[5]; //diclaration and creation
x[0]=35; //initialization array element
x[1]=30;
x[2]=13;
x[3]=31;
x[4]=113;
//display every array element
System.out.println("element of array[0] is :"+x[0]);
System.out.println("element of array[1] is :"+x[1]);
System.out.println("element of array[2] is :"+x[2]);
System.out.println("element of array[3] is :"+x[3]);
System.out.println("element of array[3] is :"+x[4]);
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
element of array[0] is :35 element of array[1] is :30 element of array[2] is :13 element of array[3] is :31 element of array[4] is :113
Program 2
class Array_demo{
public static void main (String args[]){
int[] arr;//array declaration
arr=new int[10]; //array creation, array length - 10 integer type
arr[0]=124;//array initialization - firstt element
arr[1]=24;
arr[2]=14;
arr[3]=12;
arr[4]=104;
arr[5]=120;
arr[6]=129;
arr[7]=195;
arr[8]=145;
arr[9]=624; //last element
//display array elements
System.out.println("Element of index[0] is :"+arr[0]);
System.out.println("Element of index[1] is :"+arr[1]);
System.out.println("Element of index[2] is :"+arr[2]);
System.out.println("Element of index[3] is :"+arr[3]);
System.out.println("Element of index[4] is :"+arr[4]);
System.out.println("Element of index[5] is :"+arr[5]);
System.out.println("Element of index[6] is :"+arr[6]);
System.out.println("Element of index[7] is :"+arr[7]);
System.out.println("Element of index[8] is :"+arr[8]);
System.out.println("Element of index[9] is :"+arr[9]);
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
element of index[0] is :124 element of index[1] is :24 element of index[2] is :14 element of index[3] is :12 element of index[4] is :104 element of index[5] is :120 element of index[6] is :129 element of index[7] is :195 element of index[8] is :145 element of index[9] is :624
Display of element of the array using for loop
we can display elements from the array using for loop as follows
for (int i=1; i<=5; i++){
System.out.print(array_name(i));
}
program 1
class arraywithfor{
public static void main(String args[]){
int[] num; //declaration of Array
num=new int[6]; // Creation of Array
num[0]=115; //initiation of element for index 0
num[1]=172; //initiation of element for index 1
num[2]=193; //initiation of element for index 2
num[3]=607; //initiation of element for index 3
num[4]=745; //initiation of element for index 4
num[5]=100; //initiation of element for index 5
System.out.println("Element of Array");
for(int i=0; i<=5; i++){
System.out.println(num[i]);
//Display array element using for loop
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
Element of Array 115 172 193 607 745 100
Display of element using for loop in Array with array length
Method 1
for(i=0; i<=array.length-1; i++) { //i<=array.length-1
System.out.println(array_name[i]);
}
Method 2
for(i=0; i<array.length; i++) { //i<array.length
System.out.println(array_name[i]);
}
Program 1
class array1d{
public static void main (String args[]){
int anArray[]=new int[6];
anArray[0]=345;
anArray[1]=145;
anArray[2]=365;
anArray[3]=349;
anArray[4]=355;
anArray[5]=745;
for(int i=0; i<=anArray.length-1; i++){
System.out.println(anArray[i]);
}
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
345 145 365 349 355 745
Display of element using Enhanced for loop in Array
we can display elements from the array using enhanced for loop as follows
for int i:array_name{
System.out.print(i);
}
Program 1
class arrayforloop2{
public static void main(String args[]){
int[] num;//declaration of Array
num=new int[6];// Creation of Array
num[0]=110;//initiation of element for index 0
num[1]=142;//initiation of element for index 1
num[2]=153;//initiation of element for index 2
num[3]=607;//initiation of element for index 3
num[4]=745;//initiation of element for index 4
num[5]=100;//initiation of element for index 5
System.out.println("Element of Array");
for(int i:num){
System.out.println(i);
//Display array element using for loop
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
Element of Array 110 142 153 607 745 100
Array and while loop in Java
we can display elements from the array using while loop as follows
while(i<=5){
System.out.print(Array_name[i]);
}
Program 1
class Array_whileloop{
public static void main(String args[]){
int marks[]={45,67,65,82,49,97}; // Array declaration and initiation
int i=0; //Start with zero for first array index
while(i<=5){//last Array index 5
System.out.println(marks[i]);
i++;
}
}
}
When the above code is executed, it produces the following results:
45 67 65 82 49 97
Similar post
One dimensional array in C language
One dimensional array in C++ language
Two dimension array in Java language
Two dimension array in C language
Two dimension array in C++ language
Three dimension array in Java language
Three dimension array in C language
Three dimension array in C++ language
Suggested for you
for loop in Java language
while loop in Java language
Do-while loop in Java language
Enhanced for loop in Java language